Glaucoma, a leading cause of blindness worldwide, has long posed significant challenges in ophthalmology. Traditional surgical approaches, while effective, often come with substantial risks and a lengthy recovery. However, the advent of Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (MIGS) has revolutionized the treatment landscape, offering a safer, more efficient, and less invasive alternative for managing this chronic eye condition. This blog explores the transformative impact of MIGS on glaucoma surgery and patient care.
Understanding Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, typically due to increased intraocular pressure (IOP). If left untreated, this damage can lead to irreversible vision loss. Managing IOP is crucial in preventing the progression of glaucoma, and this is where surgical intervention becomes necessary when medications and laser treatments are insufficient.
The Evolution of Glaucoma Surgery
Traditional Surgery: The Legacy Approach
Historically, surgical treatments for glaucoma, such as trabeculectomy and tube shunt implants, have been the mainstays. These procedures aim to create new drainage pathways for aqueous humor, the fluid in the eye, to reduce IOP. While effective, these surgeries are invasive, requiring significant tissue manipulation and carrying risks such as infection, bleeding, and prolonged recovery times.
The Advent of MIGS: A Paradigm Shift
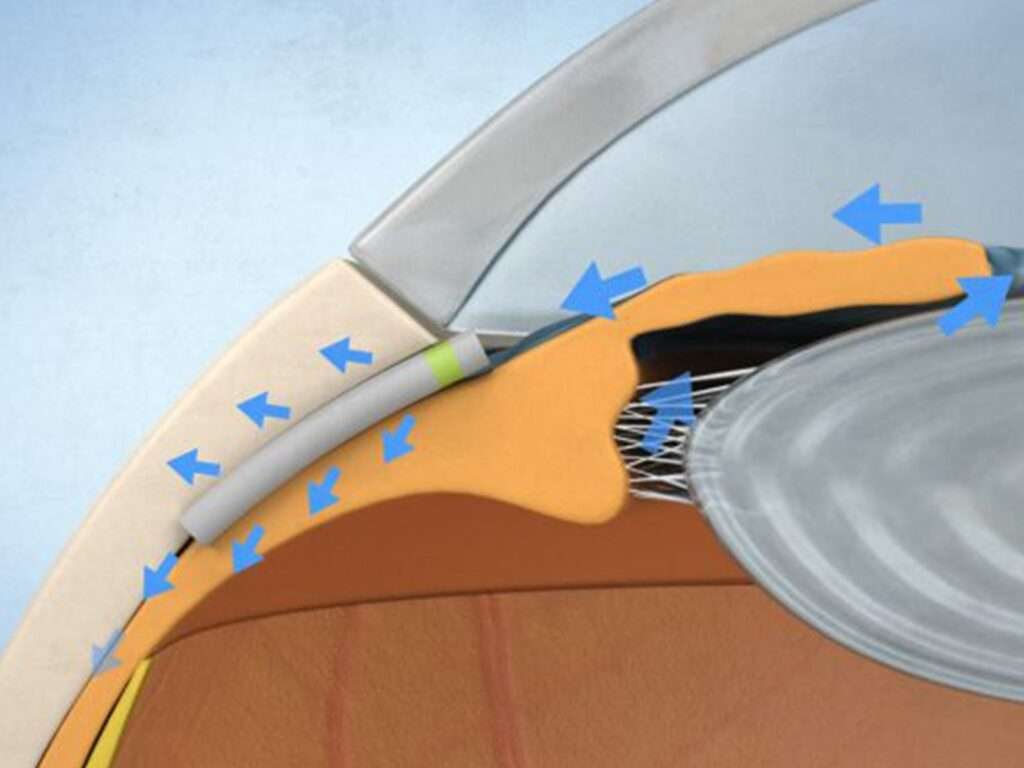
Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (MIGS) emerged in the early 2000s, introducing a new era in glaucoma treatment. MIGS techniques focus on achieving IOP reduction with minimal disruption to the eye’s anatomy. These procedures utilize microscopic instruments and implants, offering a safer and more patient-friendly alternative to traditional surgery.
Key MIGS Techniques and Devices
iStent
The iStent is a tiny, titanium device implanted into the trabecular meshwork to improve aqueous humor outflow. As one of the first MIGS devices approved by the FDA, the iStent has demonstrated significant success in lowering IOP with a favorable safety profile.
Trabectome
The Trabectome procedure involves the use of an electrosurgical handpiece to remove a portion of the trabecular meshwork, enhancing fluid drainage. This technique is performed through a small corneal incision, reducing the risk of complications associated with more invasive surgeries.
Xen Gel Stent
The Xen Gel Stent is a soft, gelatin-based implant inserted into the subconjunctival space. It creates a new drainage pathway for aqueous humor, effectively lowering IOP with minimal tissue damage. Its minimally invasive nature allows for quicker recovery and fewer postoperative complications.
Hydrus Microstent
The Hydrus Microstent, a flexible, crescent-shaped device, is implanted in the Schlemm’s canal. It serves to widen the canal and improve outflow. This device has shown promise in providing sustained IOP reduction, often in combination with cataract surgery.
Benefits of MIGS
Safety and Efficacy
MIGS procedures significantly reduce the risk of complications compared to traditional surgeries. The minimally invasive nature of these techniques minimizes tissue trauma, leading to a lower incidence of infection, bleeding, and other adverse events.
Faster Recovery
Patients undergoing MIGS typically experience a quicker recovery time. The less invasive approach allows for a more rapid return to normal activities, improving overall patient satisfaction and quality of life.
Versatility
MIGS procedures can be tailored to the individual needs of patients, making them suitable for a wide range of glaucoma severities. They can also be combined with cataract surgery, offering a dual benefit for patients with both conditions.
Patient Comfort
The reduced invasiveness of MIGS techniques translates to less postoperative discomfort and fewer follow-up visits. This improves the overall treatment experience for patients, making glaucoma management more manageable and less daunting.
The Future of MIGS
The field of MIGS continues to evolve, with ongoing research and development aimed at enhancing the efficacy and safety of these procedures. Innovations in device design and surgical techniques hold the promise of even better outcomes for glaucoma patients.
Integration with Advanced Technologies
Future advancements may see the integration of MIGS with cutting-edge technologies such as robotic surgery, real-time imaging, and personalized medicine. These innovations could further refine the precision and effectiveness of glaucoma treatments.
Expanded Indications
As our understanding of glaucoma and its pathophysiology grows, the indications for MIGS may expand. This could potentially include earlier intervention in the disease process, offering preventative benefits and reducing the overall burden of glaucoma.
Conclusion
Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (MIGS) has undoubtedly revolutionized the approach to glaucoma treatment. By offering a safer, more efficient, and patient-friendly alternative to traditional surgery, MIGS has transformed the landscape of glaucoma care. As technology continues to advance, the future of MIGS looks bright, promising even better outcomes and improved quality of life for glaucoma patients worldwide.
For those dealing with glaucoma or caring for someone who is, the evolution of MIGS offers hope and a path to better, more manageable treatment options. As always, consult with a qualified ophthalmologist to explore the best surgical options for your individual needs.

