In the intricate landscape of health, diabetes stands as a formidable adversary, affecting millions worldwide. Among its various complications, diabetic retinopathy emerges as a silent yet potent threat to vision. Particularly in India, where the prevalence of diabetes is soaring, the risk of blindness due to diabetic retinopathy looms large. In this blog, we delve into the nuances of diabetic retinopathy, its impact on eyes, and why it poses a significant concern for the Indian population. Additionally, we explore the diverse treatment options available to manage this condition.
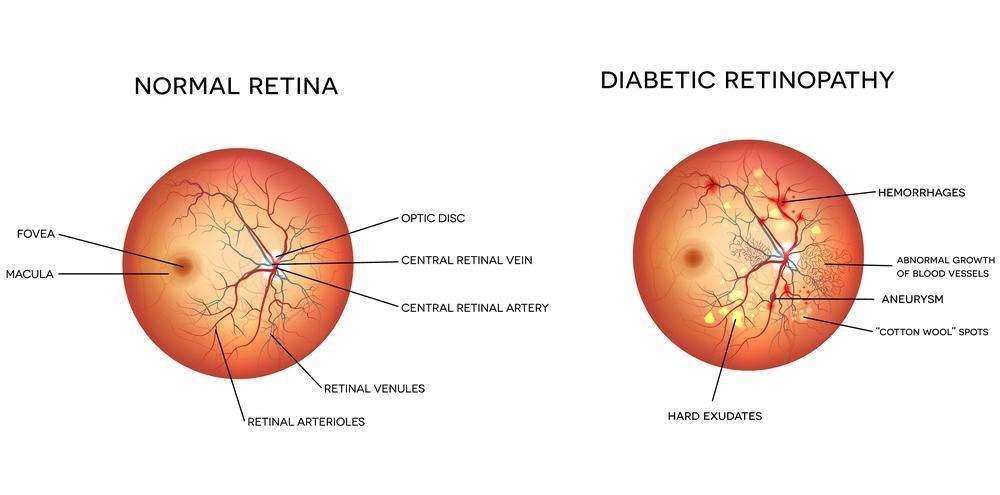
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy: Diabetic retinopathy is a diabetes-induced complication that affects the eyes. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue lining the back of the eye. This damage can lead to various vision problems, ranging from mild blurriness to complete blindness if left untreated.
The progression of diabetic retinopathy typically occurs in stages:Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR): In this early stage, blood vessels in the retina weaken and may leak fluid or blood into the retina, causing it to swell and impairing vision.
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR): As the condition advances, new abnormal blood vessels may grow on the surface of the retina. These fragile vessels are prone to bleeding, leading to further vision loss and potentially retinal detachment.
Why is the Indian Population at Higher Risk?
India is grappling with a diabetes epidemic, with millions of people diagnosed with the condition. Several factors contribute to the increased risk of diabetic retinopathy and subsequent blindness in the Indian population:
Genetic Predisposition: Indians are genetically predisposed to developing diabetes, making them more susceptible to its complications, including diabetic retinopathy.
Poor Diabetes Management: Limited access to healthcare, lack of awareness, and inadequate diabetes management contribute to uncontrolled blood sugar levels, exacerbating the risk of diabetic retinopathy.
Urbanization and Lifestyle Changes: Rapid urbanization and sedentary lifestyles have led to a surge in obesity and diabetes prevalence, further fueling the diabetic retinopathy burden.
Treatment Options for Diabetic Retinopathy:
Early detection and timely intervention are crucial in managing diabetic retinopathy and preventing vision loss. Several treatment modalities are available, depending on the severity of the condition:
Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and maintaining optimal blood sugar levels, can help slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy.
Medications: In cases of macular edema (swelling of the macula, the central part of the retina), intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF drugs or steroids may be prescribed to reduce swelling and preserve vision.
Laser Therapy: Laser photocoagulation is a common treatment for diabetic retinopathy. It involves using a laser to seal leaking blood vessels or destroy abnormal blood vessels to prevent further damage to the retina.
Vitrectomy: In advanced cases of diabetic retinopathy with significant bleeding or retinal detachment, a surgical procedure called vitrectomy may be performed to remove blood and scar tissue from the eye.
Conclusion: Diabetic retinopathy poses a significant threat to vision, particularly in populations with a high prevalence of diabetes like India. Awareness, early detection, and proactive management are essential in mitigating the impact of this sight-threatening complication. By embracing a holistic approach to diabetes care and leveraging the available treatment options, we can safeguard the precious gift of sight and improve the quality of life for individuals living with diabetes.

